3.1 string 容器
3.1.1 string基本概念
本质:
。string是C++风格的字符串,而string本质上是一个类
stringi和char*区别:
·char*是一个指针
·string是一个类,类内部封装了char,管理这个字符串,是一个char 型的容器。
特点:
string类内部封装了很多成员方法I
例如:查找find,拷贝copy,删除delete替换replace,插入insert
string管理chr*所分配的内存,不用担心复制越界和取值越界等,由类内部进行负责
3.1.2 string构造函数
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std;void test () const char * str = "hello world" ;string s2 (str) ;string s3 (s2) ;string s4 (10 , 'a' ) ;int main () test ();
3.1.3 string赋值操作
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 void test01 () "hello world" ;'a' ;4. assign ("hello c++" );5. assign ("hello c++" , 5 );4. assign (str5);4. assign (10 ,'w' );
3.1.4 字符串拼接
在字符串尾拼接字符串
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void test02 () "wo" ;"aiwanyouxi" ;':' ;"LOL" ;"I" ;3. append (" love " );3. append ("game abcde" , 4 );3. append (str2);3. append (str2, 0 , 3 );
3.1.5 string查找和替换
功能描述:
查找:查找指定字符是否存在
,替换:在指定的位置替换字符串
函数原型:
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void test03 () "abcdefgde" ;int pos = str1.f ind("de" ); 1. rfind ("de" ); void test04 () "abcdefg" ;1. replace (1 ,3 ,"111" );
3.1.6 string字符串比较
功能描述:
·字符串之间的比较
比较方式:
·字符串比较是按字符的ASCI码进行对比
=返回0
>返回1
<返回-1
函数原型:
int compare(const string &s)const; //与字符串s比较
int compare(const char *s)const; //与字符串s比较
1 2 3 4 5 6 void test05 () "hello" ;"hfllo" ;1. compare (str2) << endl;
3.1.7 字符存取
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 void test06 () "hello" ;for (int i = 0 ; i < str1. size (); i++)" " ;for (int i = 0 ; i < str1. size (); i++)1. at (i) << " " ;0 ] = 'x' ;1 ] = 'x' ;
3.1.8 string插入和删除
功能描述:
·对string字符串进行插入和删除字符操作
函数原型:
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 void test07 () "hello" ;1. insert (1 , "111" );1. erase (1 , 3 );
3.1.9 string子串
功能描述:
·从字符串中获取想要的子串
函数原型:
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 void test08 () "hello" ;1. substr (1 , 3 );int pos = str1.f ind('o' );1. substr (0 , pos);
3.2 vector容器
3.2.1 vector基本概念
功能:
·vector数据结构和数组非常相似,也称为单端数组
vector.与普通数组区别:
·不同之处在于数组是静态空间,而vectori可以动态扩展
动态扩展:
·并不是在原空间之后续接新空间,而是找更大的内存空间,然后将原数据拷贝新空间,释放原空间
img
3.2.2 vector构造函数
功能描述:
·创建vector容器
函数原型:
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 void printVector (vector<int >& v) for (vector<int >::iterator it = v.begin (); it != v.end () ; it++)" " ;void test01 () int >v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)1. push_back (i);printVector (v1);int >v2 (v1. begin (),v1. end ());printVector (v2);int >v3 (10 , 100 );printVector (v3);int >v4 (v3);printVector (v4);
3.2.3 vector赋值操作
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 void test02 () int >v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)1. push_back (i);printVector (v1);int >v2 = v1;printVector (v2);int >v3;3. assign (v1. begin (),v1 .end ());printVector (v3);int >v4;4. assign (10 ,100 );printVector (v4);
3.2.4 容量和大小
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 void test03 () int >v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)1. push_back (i);printVector (v1);1. empty () << endl;1. capacity () << endl;1. size () << endl;1. resize (15 );printVector (v1);1. empty () << endl;1. capacity () << endl;1. size () << endl;1. resize (5 );printVector (v1);1. empty () << endl;1. capacity () << endl;1. size () << endl;
3.2.5 插入和删除
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 void test04 () int >v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)1. push_back (i);printVector (v1);1. pop_back ();1. insert (v1. begin (), 100 );printVector (v1);1. insert (v1. begin (), 2 , 100 );printVector (v1);1. erase (v1. begin ());printVector (v1);1. erase (v1. begin (),v1. end ());printVector (v1);1. clear ();
3.2.6 数据存取
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 void test05 () int >v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)1. push_back (i);printVector (v1);for (int i = 0 ; i < v1. size (); i++)" " ;for (int i = 0 ; i < v1. size (); i++)1. at (i) << " " ;1.f ront() << endl;1. back () << endl;
3.2.7 互换容器
img
巧用swap可以收缩内存空间
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 void test06 () int >v1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)1. push_back (i);printVector (v1);int >v2;for (int i = 10 ; i > 0 ; i--)2. push_back (i);printVector (v2);1. swap (v2);printVector (v1);printVector (v2);1. resize (3 );vector <int >(v1).swap (v1);1. capacity () << endl;
3.2.8 预留空间
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void test07 () int >v;reserve (100000 );int num = 0 ;int * p = NULL ;for (int i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++)push_back (i);if (p!=&v[0 ])0 ];
3.3 deque容器
3.3.1 deque容器基本概念
功能:
·双端数组,可以对头端进行插入删除操作
deque与vector区别:
·vector对于头部的插入删除效率低,数据量越大,效率越低
·deque相对而言,对头部的插入删别除速度回vector快
·vector访问元素时的速度会比deque快这和两者内部实现有关
deque内部工作原理:
dequer内部有个中控器,维护每段缓冲区中的内容,缓冲区中存放真实数据
中控器维护的是每个缓冲区的地址,使得使用deque时像一片连续的内存空间
deque容器的迭代器也是支持随机访问的
3.3.2 deque构造函数
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 void printDeque (const deque<int > &d) for (deque<int >::const_iterator it = d.begin (); it != d.end (); it++)" " ;void test01 () int > d1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)1. push_back (i);printDeque (d1);deque<int > d2 (d1. begin(), d1. end()) ;printDeque (d2);deque<int > d3 (10 , 100 ) ;printDeque (d3);deque<int > d4 (d3) ;printDeque (d4);
3.3.3 赋值操作
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 void test02 () int > d1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)1. push_back (i);printDeque (d1);int > d2;printDeque (d2);int > d3;3. assign (d1. begin (), d1. end ());printDeque (d3);int > d4;4. assign (10 , 100 );printDeque (d4);
3.3.4 大小操作
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void test03 () int > d1;for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++)1. push_back (i);printDeque (d1);1. empty () << endl;1. size () << endl;1. resize (15 );1. resize (16 ,1 );1. resize (5 );printDeque (d1);
3.3.5 插入和删除
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 void test04 () int > d1;1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (20 );1. push_front (100 );1. push_front (200 );printDeque (d1);1. pop_back ();printDeque (d1);1. pop_front ();printDeque (d1);1. insert (d1. begin (), 1000 );printDeque (d1);1. insert (d1. begin (), 2 ,2000 );printDeque (d1);int >d2;2. push_back (1 );2. push_back (2 );2. push_back (3 );1. insert (d1. begin (), d2. begin (), d2. end ());printDeque (d1);1. erase (d1. begin ());printDeque (d1);int >::iterator it = d1. begin ();1. erase (it);printDeque (d1);1. clear ();printDeque (d1);
3.3.6 数据存取
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 void test05 () int > d1;1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (20 );for (int i = 0 ; i < d1. size (); i++)" " ;1. at (i) << " " ;1.f ront() << endl;1. back () << endl;
3.3.7 排序
img
对于支持随机访问的迭代器的容器,都可以利用sot算法直接对其进行排序
vector容器也可以利用sort进行排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 void test06 () int > d1;1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (40 );1. push_back (30 );1. push_back (60 );1. push_back (50 );1. push_back (20 );printDeque (d1);sort (d1. begin (), d1. end ());printDeque (d1);
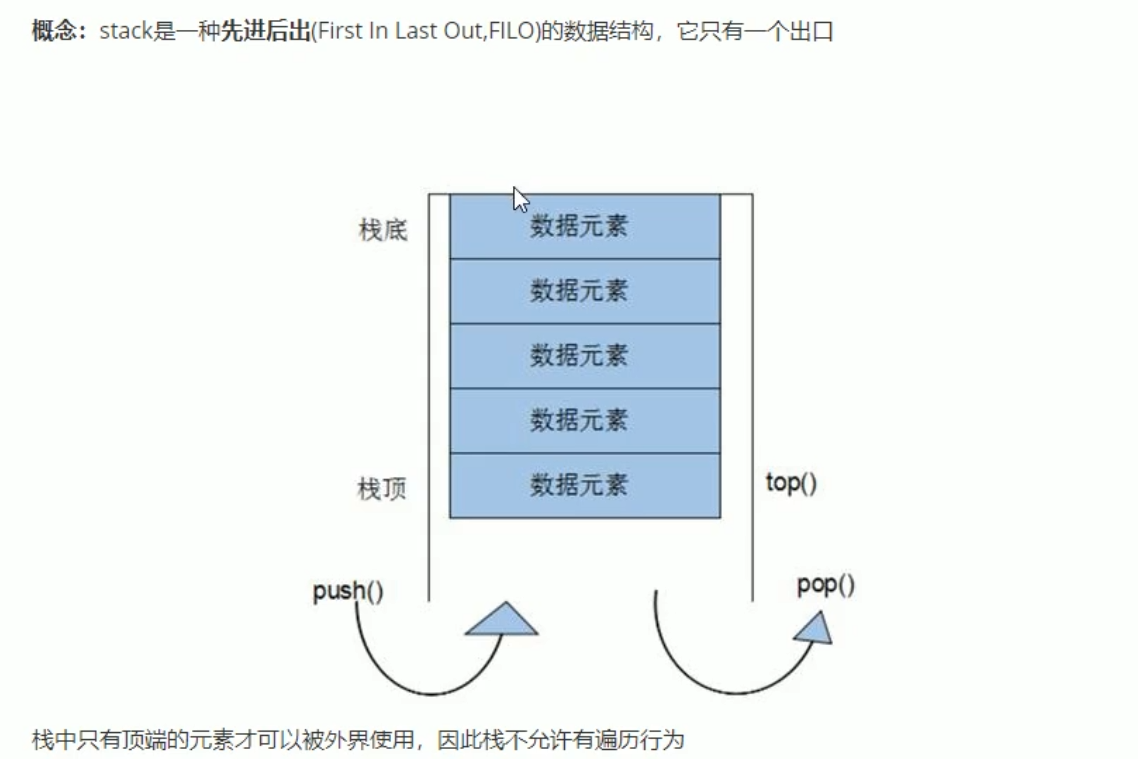
3.4 stack容器
img
栈中只有顶端的元素才可以被外界使用,因此栈不允许有遍历行为
栈中进入数据称为-入栈push
栈中弹出数据称为一出栈pop
3.4.1 stack常用接口
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include <iostream> #include <stack> using namespace std;void test () int >s;push (10 );push (20 );push (30 );push (40 );while (!s.empty ())top () << endl;pop ();size () << endl;;int main () test ();
3.5 queue 容器
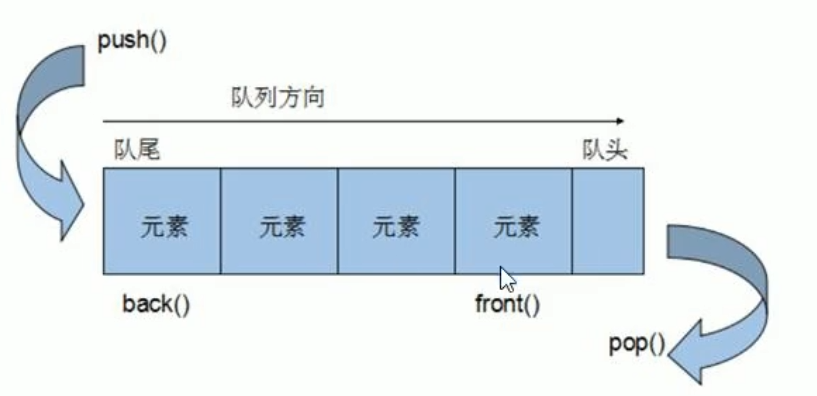
概念:Queue是一种先进先出(First In First
Out,FIFO)的数据结构,它有两个出口
队列Queue符合先进先出
只有队头和队尾能被外界访问,因此不允许有遍历行为
img
入队-push
出队-pop
返回队头元素-front
返回队尾元素-back
判断队是否为空-empty
返回队列大小-size
3.5.1 常用接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std;class Person public :Person (string m_name, int m_age) :name (m_name), age (m_age) {}int age;void test () Person p1 ("tangseng" , 30 ) ;Person p2 ("sunwukong" , 1000 ) ;Person p3 ("zhubajie" , 900 ) ;Person p4 ("shaseng" , 800 ) ;push (p1);push (p2);push (p3);push (p4);size () << endl;while (!q.empty ())front ().name << " " << q.front ().age << endl;back ().name << " " << q.back ().age << endl;pop ();size () << endl;
3.6 list 容器
功能:将数据进行链式存储
链表(st)是一种物理存储单元上非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接实现的
链表的组成:链表由一系列结点组成
结点的组成:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域
STL中的链表是一个双向循环链表
由于链表的存储方式并不是连续的内存空间,因此链表s中的迭代器只支特前移和后移,属于双向迭代器
list的优点:
·采用动态存储分配,不会造成内存浪费和溢出
·链表执行插入和删除操作十分方便,修改指针即可,不需要移动大量元素
list的缺点:
·链表灵活,但是空间(指针域)和时间(遍历)额外耗费较大
List有一个重要的性质,插入操作和删除操作都不会造成原有ist迭代器的失效,这在vector;是不成立的。
总结:STL中List和vector是两个最常被使用的容器,各有优缺点
3.6.1 Iist构造函数.
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <iostream> #include <list> using namespace std;void PrintList (const list<int >& L) for (list<int >::const_iterator it = L.begin (); it != L.end (); it++)" " ;void test () int > L1;1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (20 );1. push_back (30 );1. push_back (40 );PrintList (L1);list<int > L2 (L1. begin(), L1. end()) ;PrintList (L2);list<int > L3 (L1) ;PrintList (L3);list<int > L4 (10 , 1000 ) ;PrintList (L4);int main () test ();
3.6.2 Iist赋值和交换
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 void test02 () int > L1;1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (20 );1. push_back (30 );1. push_back (40 );PrintList (L1);int > L2;PrintList (L2);int > L3;3. assign (L1. begin (), L1. end ());PrintList (L3);int > L4;4. assign (10 , 1000 );PrintList (L4);1. swap (L4);PrintList (L1);PrintList (L4);
3.6.3 Iist大小操作
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 void test03 () int > L1;1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (20 );1. push_back (30 );1. push_back (40 );PrintList (L1);1. empty () << endl;1. size () << endl;1. resize (10 ,100 );PrintList (L1);1. resize (5 );PrintList (L1);
3.6.4 Iist插入和删除
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 void test04 () int > L1;1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (20 );1. push_back (30 );1. push_back (40 );1. push_front (100 );1. push_front (200 );1. push_front (300 );PrintList (L1);1. pop_back ();PrintList (L1);1. pop_front ();PrintList (L1);1. insert (L1. begin (),1000 );PrintList (L1);int >::iterator it = L1. begin ();1. insert (++it,1000 );1. begin ();1. erase (it);PrintList (L1);1. remove (1000 );PrintList (L1);1. clear ();PrintList (L1);
3.6.5 Iist数据存取
img
验证迭代器是不支持随机访问的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 void test05 () int > L1;1. push_back (10 );1. push_back (20 );1. push_back (30 );1. push_back (40 );1.f ront() << endl;1. back () << endl;
3.6.6 Iist反转和排序
img
所有不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,不可以用标准算法
不支持随机访问迭代器的容器,内部会提供对应一些算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 bool myCompare (int num1,int num2) return num1 > num2;void test05 () int > L1;1. push_back (50 );1. push_back (20 );1. push_back (60 );1. push_back (40 );1. push_back (70 );PrintList (L1);1. reverse ();PrintList (L1);1. sort ();PrintList (L1);1. sort (myCompare);PrintList (L1);
3.7 set/multiset容器
3.7.1 概念
简介:
·所有元素都会在插入时自动被排序
本质:
·set/multiset属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现。
set和multiset区别:
。set不允许容器中有重复的元素
multiset允许容器中有重复的元素
3.7.2 set构造和赋值
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <iostream> #include <set> using namespace std;void printSet (set<int >& s) for (set<int >::iterator it = s.begin (); it != s.end (); it++)" " ;void test01 () int >s1;1. insert (10 );1. insert (20 );1. insert (30 );1. insert (40 );printSet (s1);int >s2 (s1);printSet (s2);int >s3;printSet (s3);int main () test01 ();
3.7.3 set大小和交换
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 void test02 () int >s1;1. insert (10 );1. insert (20 );1. insert (30 );1. insert (40 );printSet (s1);1. empty () << endl;1. size () << endl;int >s2;2. insert (100 );2. insert (200 );2. insert (300 );2. insert (400 );printSet (s2);1. swap (s2);printSet (s1);printSet (s2);
3.7.4 set插入和删除
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 void test03 () int >s1;1. insert (10 );1. insert (20 );1. insert (30 );1. insert (40 );printSet (s1);1. erase (s1. begin ());printSet (s1);1. erase (30 );printSet (s1);1. clear ();printSet (s1);
3.7.5 set查找和统计
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void test04 () int >s1;1. insert (10 );1. insert (20 );1. insert (30 );1. insert (40 );printSet (s1);int >::iterator pos = s1.f ind(30 );if (pos!=s1. end ())int num = s1. count (30 );
3.7.6 set和multiset区别
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 void test05 () int >s1;int >::iterator, bool > ret = s1. insert (10 );1. insert (10 );int >ms;insert (10 );insert (10 );for (multiset<int >::iterator it = ms.begin (); it != ms.end (); it++)" " ;
3.7.7 pair对组创建
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 void test06 () int >p ("Tom" , 20 );" " << p.second << endl;int >p2 = make_pair ("Tom" , 20 );2.f irst << " " << p2. second << endl;
3.7.8 set容器排序
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 class MyCompare public :bool operator () (int num1,int num2) const {return num1 > num2;void test07 () int >s1;1. insert (10 );1. insert (20 );1. insert (30 );1. insert (40 );1. insert (50 );1. insert (60 );printSet (s1);int ,MyCompare>s2;2. insert (10 );2. insert (20 );2. insert (30 );2. insert (40 );2. insert (50 );2. insert (60 );for (set<int , MyCompare>::iterator it = s2. begin (); it != s2. end (); it++)" " ;class comparePerson public :bool operator () (const Person&p1,const Person&p2) const {return p1. age > p2. age;void test08 () Person p1 ("刘备" , 24 ) ;Person p2 ("关羽" , 30 ) ;Person p3 ("张飞" , 25 ) ;Person p4 ("赵云" , 20 ) ;1. insert (p1);1. insert (p2);1. insert (p3);1. insert (p4);for (set<Person, comparePerson>::iterator it = s1. begin (); it != s1. end (); it++)" " << it->age << " " << endl;
3.8 map/multimap容器
3.8.1 map基本概念
简介:
map中所有元素都是pair
·pair中第一个元素为key(键值),起到索引作用,第二个元素为value(实值)
·所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动排序
本质:
map/multimap属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现。
优点:
·可以根据key值快速找到value值
map和multimapl区别:
·map不允许容器中有重复key值元素
multimap:允许容器中有重复key值元素
3.8.2 map构造和赋值
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 void PrintMap (map<int , int >&m) for (map<int ,int >::iterator it = m.begin (); it != m.end (); it++)" " << it->second << endl;void test01 () int , int >m;insert (pair <int , int >(1 , 10 ));insert (pair <int , int >(2 , 20 ));insert (pair <int , int >(3 , 30 ));insert (pair <int , int >(4 , 40 ));PrintMap (m);int , int >m2 (m);PrintMap (m2);int , int >m3 = m2;PrintMap (m3);
3.8.3 map大小和交换
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 void test02 () int , int >m;insert (pair <int , int >(1 , 10 ));insert (pair <int , int >(2 , 20 ));insert (pair <int , int >(3 , 30 ));insert (pair <int , int >(4 , 40 ));PrintMap (m);empty () << endl;size () << endl;int , int >m2;2. insert (pair <int , int >(12 , 120 ));2. insert (pair <int , int >(22 , 202 ));2. insert (pair <int , int >(32 , 320 ));2. insert (pair <int , int >(42 , 420 ));PrintMap (m2);swap (m2);PrintMap (m);PrintMap (m2);
3.8.4 map插入和删除
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 void test03 () int , int >m;insert (pair <int , int >(1 , 10 ));insert (make_pair (2 , 20 ));insert (map<int , int >::value_type (3 , 30 ));4 ] = 40 ;PrintMap (m);erase (m.begin ());PrintMap (m);erase (3 );PrintMap (m);erase (m.begin (), m.end ());PrintMap (m);clear ();PrintMap (m);
3.8.5 map查找和统计
img
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 void test04 () int , int >m;insert (pair <int , int >(1 , 10 ));insert (make_pair (2 , 20 ));insert (map<int , int >::value_type (3 , 30 ));4 ] = 40 ;PrintMap (m);int , int >::iterator pos = m.find (3 );" " << pos->second << endl;int num = m.count (3 );
3.8.6 map容器排序
学习目标:
·map容器默认排序规则为按照key值进行从小到大排序,掌握如何改变排序规则
主要技术点:
·利用仿函数,可以改变排序规则
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 void test05 () int , int , MyCompare>m;insert (pair <int , int >(1 , 10 ));insert (make_pair (2 , 20 ));insert (map<int , int >::value_type (3 , 30 ));4 ] = 40 ;for (map<int , int , MyCompare>::iterator it = m.begin (); it != m.end (); it++)" " << it->second << endl;